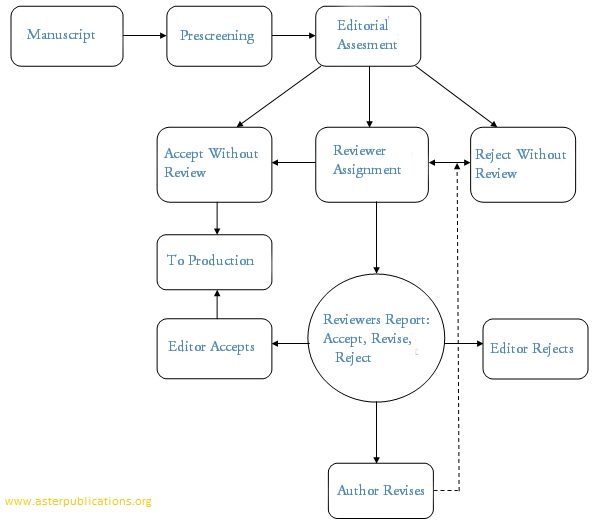
Peer Review
Peer review is the evaluation of the quality of scholarly work. After a manuscript is submitted, a journal editor screens the manuscript and decides whether or not to send it for full peer review. Only after clearing the initial screening is the manuscript sent to two or more peer reviewers who are experts on the article’s topic. Finally, journal editors or the journal’s editorial board consider the peer reviewers’ reports and make the final decision to accept or reject the manuscript for publication.
Benefit of Peer Review
Peer review is a crucial part of the scientific publishing process and provides several benefits to both authors and readers. Some of the key benefits of peer review include:
Validation of research: Peer review helps to validate research findings by subjecting them to critical evaluation by experts in the field.
Feedback and improvement: Authors receive feedback on their work, allowing them to make improvements to their research, methodology, and presentation. This can help to improve the quality of the research.
Identification of errors and flaws: Peer review helps to identify errors and flaws in research that might otherwise go unnoticed. This helps to ensure the accuracy and reliability of research findings.
Quality control: Peer review is an essential part of maintaining the quality of scientific literature. It helps to weed out low-quality research and prevent the publication of inaccurate or misleading findings.
Exposure to new ideas and research: Peer review allows researchers to learn about new ideas and research in their field, helping them to stay up-to-date and make new connections.
Overall, peer review is critical for ensuring the integrity and quality of scientific research, and helps to advance our understanding of the world around us.
Peer review helps to decide whether the work should be accepted, considered acceptable with revisions, or rejected. The goal of Peer review is to enhance the quality of the work and provide credibility to the literature in their discipline.
All the journals of ‘Aster Publications’ follow double-blind peer review process.
Double-Blind Peer Review
Double-blind peer review is a process of reviewing scholarly articles or papers where both the author and the reviewers are anonymous to each other. In this review process, the author's identity is kept confidential from the reviewers and vice versa. Double-blind peer review aims to reduce biases in the review process that could occur if reviewers knew the identity of the author, such as their gender, institution, or reputation. This type of review can increase the quality and reliability of the research by ensuring that the reviewers focus solely on the content and merit of the work.
Accepted articles are published immediately upon the final corrections of the master proof having been made. All articles are assigned a DOI number (Digital Object Identifier).
